GloVe: Global Vectors for Word Representation
一、总览
Glove, short for “Global Vectors for Word Representation”, 顾名思义,从全局角度构建word2vec.
本质做法:在MF(矩阵分解) + word2vec 的结合, 充分利用各自的优点,同时克服对应的缺点。
MF(PLSA, SVD等): 优点:充分利用全局的统计信息,构建词贡献矩阵。
缺点:在词类比任务上表现差。
Word2vec(skip-gram, cbow): 优点:利用局部的上下文窗口信息训练的词向量在词类比任务上表现不错。
缺点:没有充分利用全局的统计信息。(学习不到全局的信息)
So far, we have looked at two main classes of methods to find word embeddings.
The first set are count-based and rely on matrix factorization (e.g. LSA, HAL). While these methods effectively leverage global statistical information, they are primarily used to capture word similarities and do poorly on tasks such as word analogy, indicating a sub-optimal vector space structure.
The other set of methods are shallow window-based (e.g. the skip-gram and the CBOW models), which learn word embeddings by making predictions in local context windows. These models demonstrate the capacity to capture complex linguistic patterns beyond word similarity, but fail to make use of the global co-occurrence statistics.
整体架构
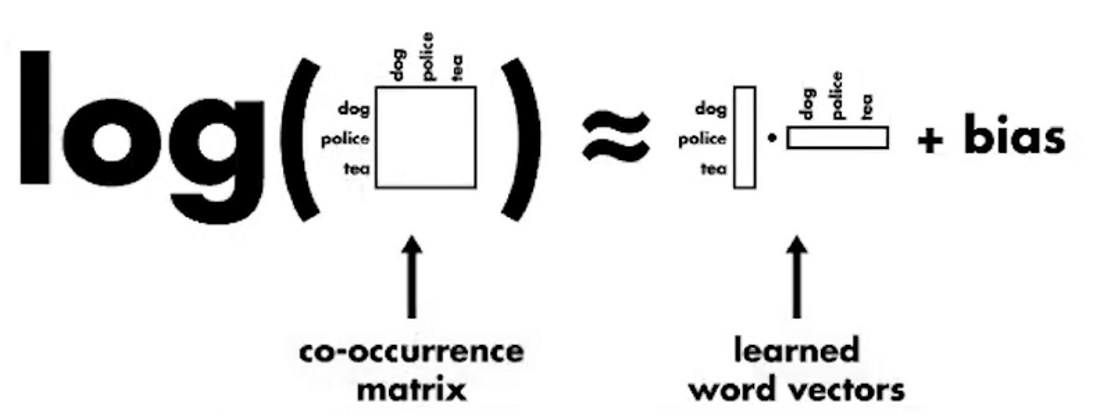
二、重点关注点
Glove的数学模型,就是到底是怎么做的?
Glove与其他模型的比较。
三、论文详细剖析
Abstract
Recent methods for learning vector space representations of words have succeeded in capturing fine grained semantic and syntactic regularities (细粒度的语法和语义规则) using vector arithmetic,but the origin of these regularities has remained opaque.(但是这些规则的源头仍然不清楚,不透明)
We analyze and make explicit the model properties needed for such regularities to emerge in word vectors.
我们分析并明确了在词向量中出现这些规则所需的模型属性。
结果就是一种新的全局对数双线性回归模型结合了两种重要的模型家族:全局矩阵分解和局部上下文窗口方法。
Introduction
Most word vector methods rely on the distance or angle between pairs of word vectors as the primary method for evaluating the intrinsic quality of such a set of word representations.
过去的评价词向量质量的方法: 大多数词向量方法依赖词向量对之间的角度或者距离作为主要评价一组词表示的内在质量的方法。
Recently, Mikolov et al. (2013c) introduced a new evaluation scheme based on word analogies (单词类比) that probes the finer structure of the word vector space by examining not the scalar distance between word vectors, but rather their various dimensions of difference.
新的方法:利用词向量空间的更精细的结构,不再是词向量之间的数量距离,而是多个维度上的不同。
For example, the analogy “king is to queen as man is to woman” should be encoded in the vector space by the vector equation king − queen = man − woman.
这个经典句子的英文表达
This evaluation scheme favors models that produce dimensions of meaning, thereby capturing the multi-clustering idea of distributed representations (Bengio, 2009).
这种评估方案有利于产生意义维度的模型,从而捕获分布式表示的多聚类思想。
Currently, both families suffer significant drawbacks. While methods like LSA efficiently leverage statistical information, they do relatively poorly on the word analogy task, indicating a sub-optimal vector space structure.
MF(LAS, SVD) 矩阵分解高效利用统计信息,但是相对的在词类比任务上表现很差。
Methods like skip-gram may do better on the analogy task, but they poorly utilize the statistics of the corpus since they train on separate local context windows instead of on global co-occurrence counts.
SG在词类比任务上表现好,但是不能很好的利用语料库的统计信息,因为他们在训练时只是运用孤立的局部上下文窗口,而不是全局的共现矩阵。
In this work, we analyze the model properties necessary to produce linear directions of meaning and argue that global log-bilinear regression models are appropriate for doing so.
我们提出了一种特定权重最小二乘法的模型,用来训练全局的词与词之间的共现矩阵计数值。
The model produces a word vector space with meaningful substructure, as evidenced by its state-of-the-art performance of 75% accuracy on the word analogy dataset.
Glove Model
1. Co-occurrence Matrix
Let $X$ denote the word-word co-occurrence matrix, where $X_{ij}$ indicates the number of times word $j$ occur in the context of word $i$.
Let $X_{i}=\sum_{k} X_{i k}$ be the number of times any word k appears in the context of word i.
Finally, let $P_{i j}=P\left(w_{j} \mid w_{i}\right)=\frac{X_{i j}}{X_{i}}$ be the probability of j appearing in the context of word i.
Compared to the raw probabilities, the ratio is better able to distinguish relevant words (solid and gas) from irrelevant words (water and fashion) and it is also better able to discriminate between the two relevant words.
相对于原始的概率,概率的比值更能够区分相关的词和不相关的词,并且能够区分两种相关的词
The above table suggests that the appropriate starting point for word vector learning should be with ratios of co-occurrence probabilities rather than the probabilities themselves.
Noting that the ratio $P_{ik}/P_{jk} $depends on three words $i$, $j$, and $k$ the most general model takes the form
$(1)$
where are word vectors and are separate context word vectors.
In this equation, the right-hand side is extracted from the corpus, and $F$ may depend on some as-of-yet unspecified parameters.
The number of possibilities for $F$ is vast, but by enforcing a few desiderata we can select a unique choice.
First, we would like $F$ to encode the information present the ratio $P_{ik}/P_{jk} $ in the word vector space. Since vector spaces are inherently linear structures, the most natural way to do this is with vector differences.
因为向量空间内在的线性结构,很自然的方式就是向量做差,于是由公式1转化为公式2
With this aim, we can restrict our consideration to those functions $F$ that depend only on the difference of the two target words, modifying Eqn. (1) to
$(2)$
Next, we note that the arguments of $F$ in Eqn. (2) are vectors while the right-hand side is a scalar. While $F$ could be taken to be a complicated function parameterized by, e.g., a neural network, doing so would obfuscate the linear structure we are trying to capture.
由于公式(2)右边的概率值是一个标量,为了简化F,防止线性结构复杂化,将公式(2)转化为公式(3), F内部参数做点积,变为标量。
To avoid this issue, we can first take the dot product of the arguments,
$(3)$
which prevents $F$ from mixing the vector dimensions in undesirable ways.
Next, note that for word-word co-occurrence matrices, the distinction between a word and a context word is arbitrary and that we are free to exchange the two roles. To do so consistently, we must not only exchange but also .
对于共现矩阵X,它是对称的,也就是说$X_{i j} = X_{j i}$ 也就是说两个单词分别作为中心词和周围词,角色互换后,共现信息还是一样的。因此F需要体现这种特性。
Our final model should be invariant under this relabeling, but Eqn. (3) is not.
However, the symmetry can be restored in two steps.
F 函数是同态的。(同态属于群论[group theory]的内容,具体可以参考 abstract algebra)
补充同态相关公式,这个地方非常关键
- HOMOMORPHISM DEFINITION:
- HOMOMORPHISM DEFINITION - VECTOR VERSION:
$F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}+w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right)=F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}\right) F\left(w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right), \forall w_{a}, v_{a}, w_{b}, v_{b} \in V$
- VECTOR HOMOMORPHISM DEFINITION WITH SUBTRACTION:
$F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}-w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right)=\frac{F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}\right)}{F\left(w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right)}, \forall w_{a}, v_{a}, w_{b}, v_{b} \in V$
- VECTOR HOMOMORPHISM DEFINITION WITH SUBTRACTION:
$F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}-w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right)=\frac{F\left(w_{a}^{T} v_{a}\right)}{F\left(w_{b}^{T} v_{b}\right)}, \forall w_{a}, v_{a}, w_{b}, v_{b} \in V$
作者解决这个问题的思路是从实数的加法群的同态到正实数的乘法群的同态
First, we require that F be a homomorphism between the groups $(\mathbb{R},+)$ and i.e.
$(4)$
which, by Eqn. (3), is solved by,
The solution to Eqn. (4) is $F$ = exp, or,
$(6)$
为了呈现交换对称性, 同时由于公式(6)中 等式右边的$\log \left(X_{i}\right)$ 独立于k, 所以将它吸收进偏执(抽象成) $b_i$ ,同时增加 $\tilde{b}_{k}$
Next, we note that Eqn. (6) would exhibit the exchange symmetry if not for the on the right-hand side. However, this term is independent of $k$ so it can be absorbed into a bias $b_i$ for $ w_i$ . Finally, adding an additional bias for restores the symmetry,
$(7)$
Eqn. (7) is a drastic simplification over Eqn. (1), but it is actually ill-defined since the logarithm diverges whenever its argument is zero. One resolution to this issue is to include an additive shift in the logarithm, $\log \left(X_{i k}\right) \rightarrow \log \left(1+X_{i k}\right)$, which maintains the sparsity of X while avoiding the divergences.
共现矩阵的分解方法有一个重要的缺陷就是它对所有共现的情况都一视同仁,即使是那些很少发生或从不发生的情况。(这也是代价巨大的原因所在,不考虑稀疏性)
The idea of factorizing the log of the co-occurrence matrix is closely related to LSA and we will use the resulting model as a baseline in our experiments.
A main drawback to this model is that it weighs all co-occurrences equally, even those that happen rarely or never.
2. Least squares Objective
We propose a new weighted least squares regression model that addresses these problems. Casting Eqn. (7) as a least squares problem and introducing a weighting function f (Xi j ) into the cost function gives us the model
$(8)$
where V is the size of the vocabulary. The weighting function should obey the following properties:
-
$f (0) = 0 $. If $f$ is viewed as a continuous function, it should vanish as $x \rightarrow 0$ fast enough that the $\lim {x \rightarrow 0} f(x) \log ^{2} x$ is finite. 也就是说$X{ij} = 0 \Longrightarrow f(X_{i j}) = 0$ 表示没有共现过的权重为0,不参加训练
-
$f (x) $ should be non-decreasing so that rareco-occurrences are not overweighted.
非减函数,因为共现次数越多,权重越大
- $f (x)$ should be relatively small for large values of $x$, so that frequent co-occurrences are not overweighted.
不能无限制的大,防止is,are,the等停用词的影响
Of course a large number of functions satisfy these properties, but one class of functions that we found to work well can be parameterized as,
$(9)$
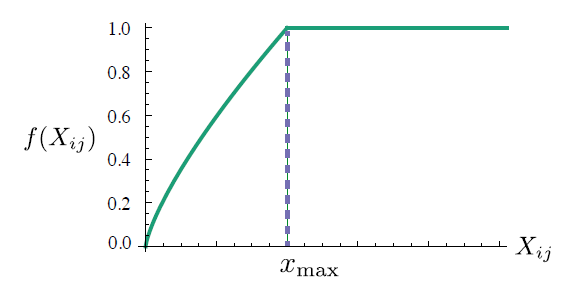
Figure 1: Weighting function $f$ with $\alpha=3 / 4$
The performance of the model depends weakly onthe cutoff, which we fix to $x_{max}$ = 100 for all our experiments. We found that $\alpha = 3/4$ gives a modest improvement over a linear version with $\alpha = 1$. Although we offer only empirical motivation for choosing the value 3/4, it is interesting that a similar fractional power scaling was found to give the best performance in (Mikolov et al., 2013a).
3. Relation to other models
Recall that for the skip-gram model, we use softmax to compute the probability of word j appears in the context of word i:
$(10)$
Most of the details of these models are irrelevant for our purposes, aside from the the fact that they attempt to maximize the log probability as a context window scans over the corpus.
训练过程是在线的,随机的,但是隐含的全局目标函数可以写成下面的形式:
Training proceeds in an on-line, stochastic fashion, but the implied global objective function can be written as,
$(11)$
To allow for efficient training, the skip-gram and ivLBL models introduce approximations to $Q_{i j}$ .
However,the sum in Eqn. (11) can be evaluated much more efficiently if we first group together those terms that have the same values for i and j,
$(12)$
where we have used the fact that the number of like terms is given by the co-occurrence matrix $X$. Recalling our notation for $X_{i}=\sum_{k} X_{i k}$ and $P_{i j}=X_{i j} / X_{i}$ we can rewrite $J$ as,
$(13)$
where $H(P_{i} ,Q_{i })$ is the cross entropy of the distributions $P_i$ and $Q_i $, which we define in analogy to $X_i$ . As a weighted sum of cross-entropy error, this objective bears some formal resemblance to the weighted least squares objective of Eqn. (8).
To begin, cross entropy error is just one among many possible distance measures between probability distributions, and it has the unfortunate property that distributions with long tails are often modeled poorly with too much weight given to the unlikely events.
首先,交叉熵误差只是概率分布之间许多可能的距离度量之一,而且它有一个不好的属性,即长尾分布的建模常常很差,对不太可能发生的事件给予了太多的权重。
Furthermore, for the measure to be bounded it requires that the model distribution $Q$ be properly normalized. 为了使测量有界,模型的分布$Q$需要被合理的归一化。
A natural choice would be a least squares objective in which normalization factors in $ Q$ and $P$ are discarded,
$(14)$
where $\hat{P}{i j}=X{i j}$ and $\hat{Q}{i j}=\exp \left(w{i}^{T} \tilde{w}_{j}\right)$ are the unnormalized distributions.
At this stage another problem emerges, namely that $X_{i j}$ often takes very large values, which can complicate the optimization. An effective remedy is to minimize the squared error of the logarithms of $\hat{P}$ and $\hat{Q}$ instead,
$\begin{aligned} \hat{J} &=\sum_{i, j} X_{i}\left(\log \hat{P}{i j}-\log \hat{Q}{i j}\right)^{2} \ &=\sum_{i, j} X_{i}\left(w_{i}^{T} \tilde{w}{j}-\log X{i j}\right)^{2} \end{aligned}$ $(15)$
we introduce a more general weighting function, which we are free to take to depend on the context word as well. The result is,
$(16)$
which is equivalent1 to the cost function of Eqn. (8), which we derived previously.
Experiments
待补充。
Conclusion
In this work we argue that the two classes of methods are not dramatically different at a fundamental level since they both probe the underlying co-occurrence statistics of the corpus, but the efficiency with which the count-based methods capture global statistics can be advantageous.
The GloVe model efficiently leverages global statistical information by training only on the nonzero elements in a wordword co-occurrence matrix, and produces a vector space with meaningful sub-structure.
We construct a model that utilizes this main benefit of count data while simultaneously capturing the meaningful linear substructures prevalent in recent log-bilinear prediction-based methods like word2vec. The result, GloVe, is a new global log-bilinear regression model for the unsupervised learning of word representations that outperforms other models on word analogy, word similarity, and named entity recognition tasks.
Inspirations
根据论文中的实验方法,我们发现:
-
词向量的维度并不是越大越好。词向量维度300~400之间其实就非常好了。
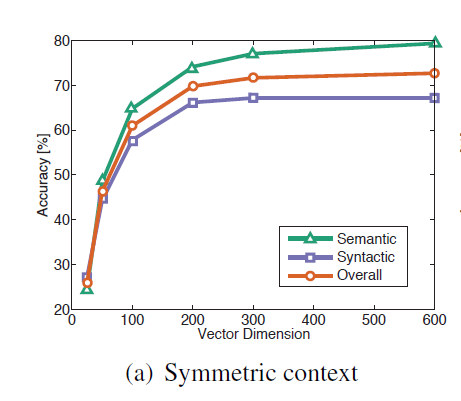
-
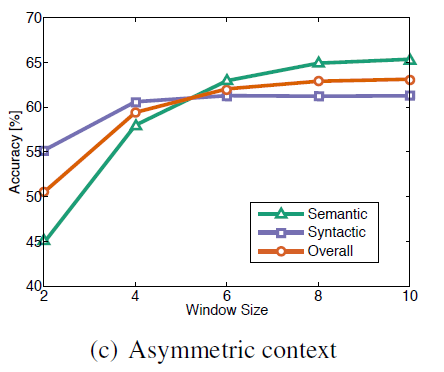
windows_size 也不是越大越好。windows_size 6~8之间都不错。
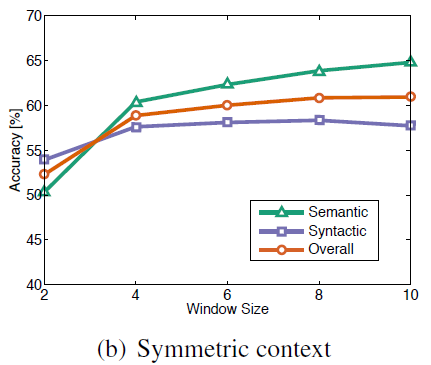
-
非对称窗口比对称窗口在语法上的效果要好。
Performance is better on the syntactic subtask for small and asymmetric context windows, which aligns with the intuition that syntactic information is mostly drawn from the immediate context and can depend strongly on word order.
-
Compared to the raw probabilities, the ratio is better able to distinguish relevant words (solid and gas) from irrelevant words (water and fashion) and it is also better able to discriminate between the two relevant words.
相对于原始的概率,概率的比值更能够区分相关的词和不相关的词,并且能够区分两种相关的词。
-
The result is a new global log-bilinear regression model that combines the advantages of the two major model families in the literature: global matrix factorization and local context window methods.
提出了一种新的对数双线性回归模型,这种模型结合全局矩阵分解和局部上下文的优点。
Coding implementation
a glove implementation of python and numpy is A GloVe implementation in Python
reference
- paper: GloVe: Global Vectors forWord Representation
-
http://building-babylon.net/2015/07/29/glove-global-vectors-for-word-representations/
- http://www.foldl.me/2014/glove-python/
- cs224n-2019 winter: cs224n-2019-notes02-wordvecs2.pdf